Audit Collection Server makale serisinin üçüncüsü ve sonuncusunda sizlere audit collection raporlarının nasıl import edildiğini ve raporların nasıl alındığını anlatacağım.Ayrıca audit database boyutunun nasıl hesaplandığını ve audit filtrelemesini tüm ayrıntılarıyla inceleyeceğim.
Yukarıda sıraladığımız özellikleri incelemeye başlamadan önce yayınlamış olduğumuz SCOM 2007 R2 Audit Collection Server (ACS) serisinin birinci ve ikinci makalesini okumak isteyenler için aşağıdaki linkleri paylaşıyorum.
http://www.mshowto.org/scom-2007-r2-audit-collection-server-acs-bolum-1.html
SCOM 2007 R2 Operation Console içerisinde yer alan Reporting bölümüne geldiğinizde Audit Collection raporlarının olmadığını göreceksiniz.Gerçekleşen audit işlemleri sonucunda oluşan verilerin raporunu almak için bu raporlara ihtiyaçımız olduğunu unutmamalıyız.
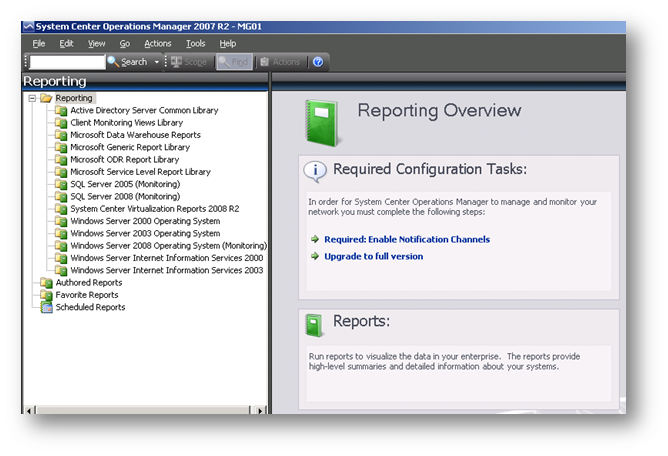
Resim-1
Bu raporlar için yapılması gereken işlemleri birazdan sıralayacağım.Audit collection raporları aslında SCOM 2007 R2 kurulum DVD’si ile gelmektedir.Yapılması gereken bu raporları Reporting Server içerisine import etmektir.İlk olarak bu raporların ve bu raporların import edilmesi için kullanılacak dosyaların kopyalanması işlemine başlıyoruz.
Önemli:Raporların import edilmesi için dosyaların kopyalanacağı klasörün SQL Server Reporting Services üzerinde olması önerilir.
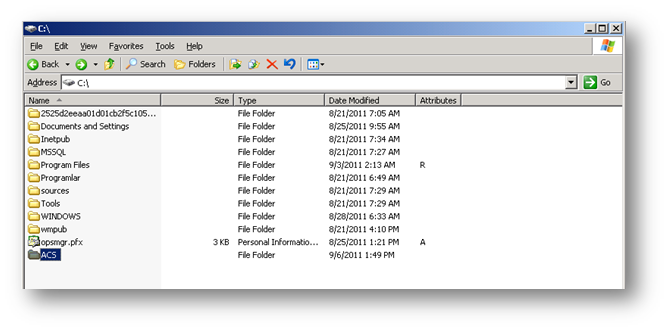
Raporların kopyalanacağı bir klasör oluşturuyoruz.Ben bu makalede C:\ sürücüsünün içerisine ACS isimli bir klasör oluşturuyorum.
Resim-2
SCOM 2007 R2 kurulum DVD’sini optik sürücüye yerleştiriyor ve ReportModels klasörünün içerisinde yer alan acs isimli klasöre giriyor içerisinde yer alan tüm dosya ve klasörleri seçip,kopyalıyorum.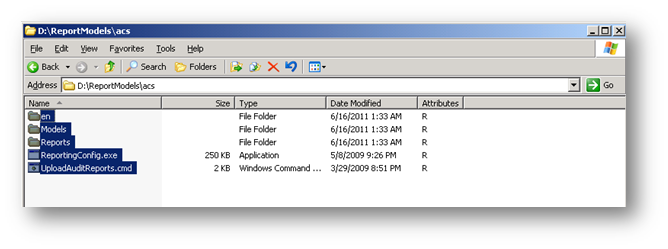
Resim-3
Kopyalamış olduğumuz dosya ve klasörleri C:\ACS klasörünün içerisine yapıştırıyoruz.
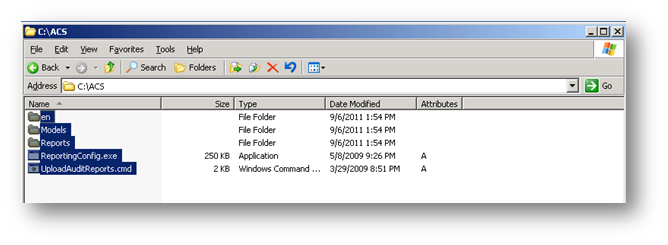
Resim-4
Audit collectiona ait raporların Reporting Server içerisine import etmek için aşağıda komut kullanılır.
UploadAuditReports “<AuditDBServer\Instance>” “<Reporting Server URL>” “<Kopyalan ACS dosyalarının bulunduğu yol>”
Komut kullanımın bir örneğini aşağıda sizler için paylaşıyorum.
UploadAuditReports.cmd OpsMgr http://OpsMgr/ReportServer C:\acs
Komut satırının kullanımını ve çıktısını aşağıdaki command prompt’ta görebilirsiniz.
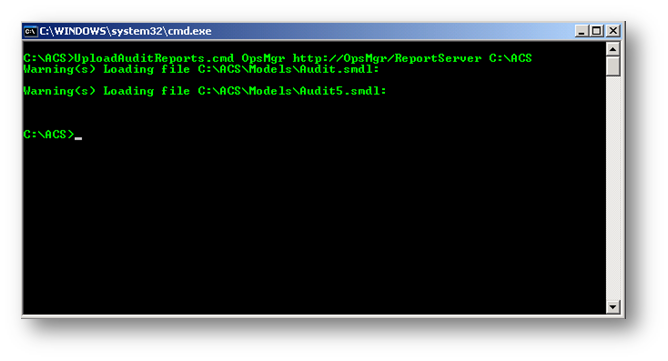
Resim-5
SCOM 2007 R2 Operation Console içerisinde yer alan Reporting bölümüne Audit Reports bölümüne geldiğini görebileceksiniz.
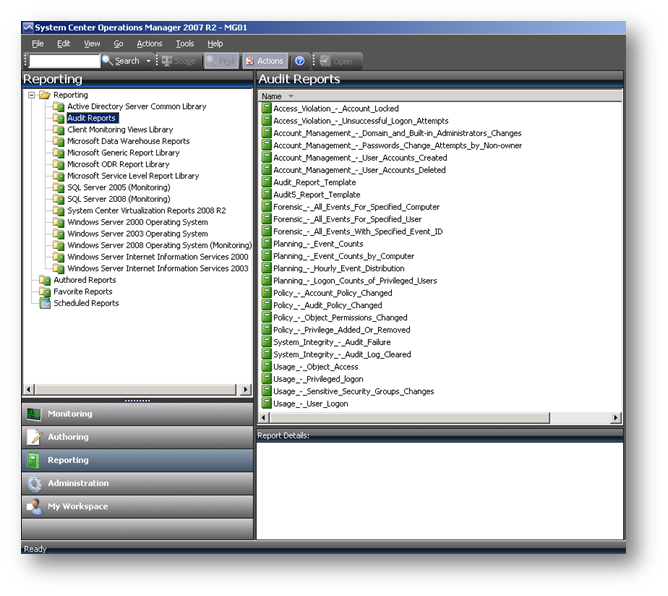
Resim-6
Herhangi bir raporun üzerine gelip farenin sağ tuşuna bastığınızda çıkan kısayol menüsünde “Open” yazısına tıkladığınızda rapor alabilirsiniz.
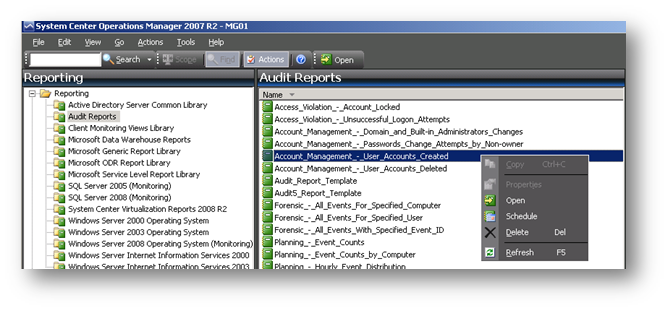
Resim-7
Raporun oluşması için kısa bir süre beklenir.
Resim-8
Aşağıda yer alan Resim-9’da oluşturulan kullanıcı hesaplarını görebilmektesiniz. “Account Management-User Accounts Created”
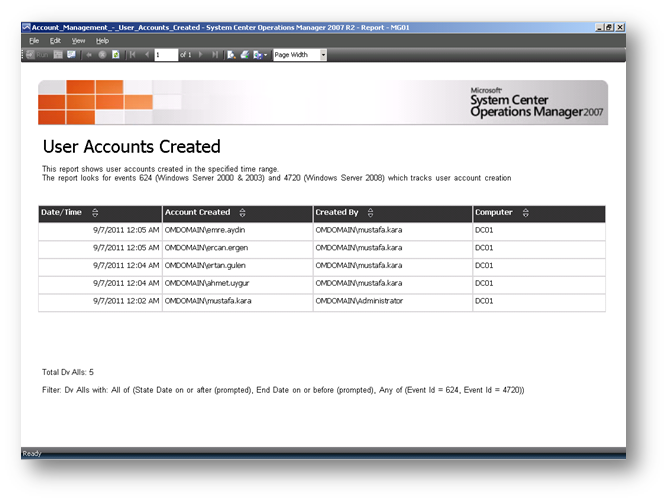
Resim-9
Resim-10’da yer alan “”Account Management-User Accounts Deleted” raporu ile silinen kullanıcı hesaplarının raporunu alabilirsiniz.
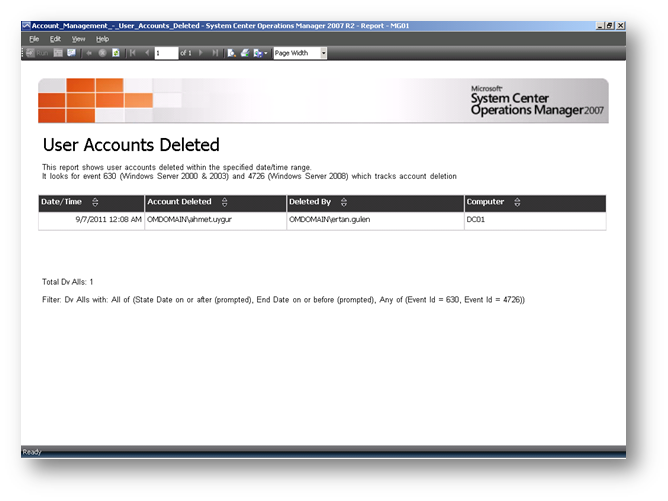
Resim-10
Resim-11’de yer alan “Access Violation-Unsuccessful Logon Attempts” raporu ilede başarısız logon teşebbüslerini görebilirsiniz.
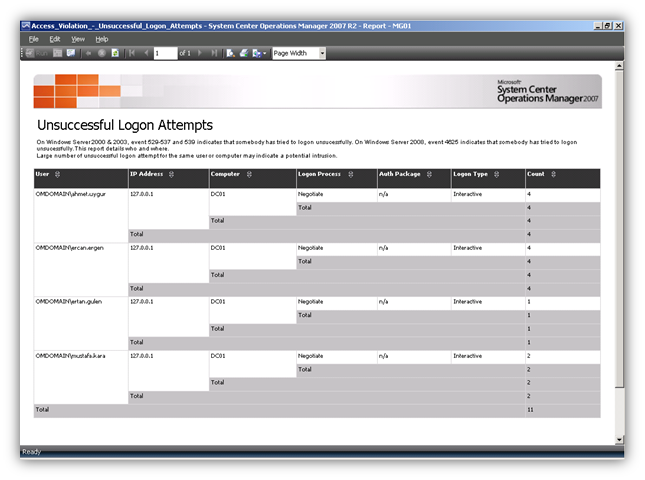
Resim-11
Aşağıda yer alan Resim-12 ve Resim-13’deki ekran görüntüleri Audit Collection Server veritabanı boyut hesaplama işlemi için kullanılan excel görüntülerine aittir.Excelde yer alan hücreleri şirketinizin yapısına ve ihtiyaçına göre doldurursanız ACS database boyutunun planlamasını yapabilirsiniz.
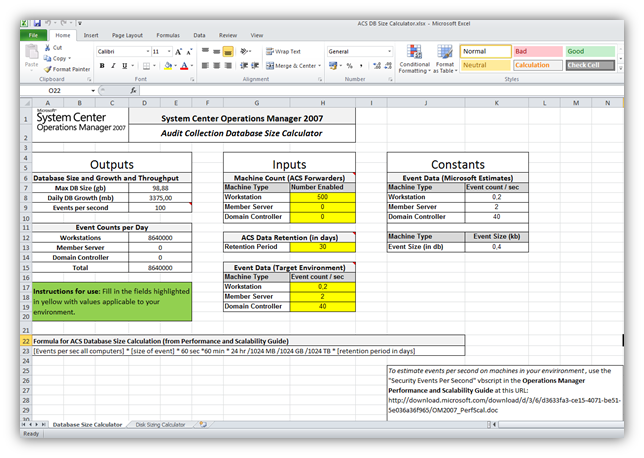
Resim-12
ACS DB Size Calculator exceli aşağıda yer alan linkten indirebilirsiniz.Excel içerisinde yer alan diğer sayfa içerisinde ise Disk Sizing Calculator bulunmaktadır.
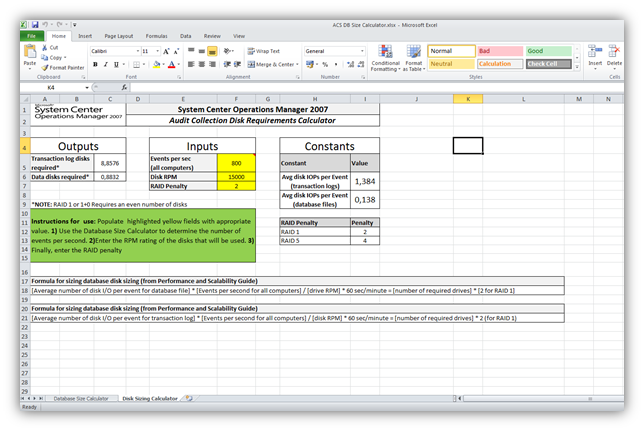
Resim-13
Audit Collection Forwarder olarak çok fazla sayıda sunucu konfigüre edilmiş ise ortaya çok yüksek boyutta bir veritabanı çıkacaktır. ACS database boyutunun daha makul miktarlara çekilmesi ,boyut azaltımı için yapılan işlem filtreleme işlemidir.Tablo-1’de Audit Collector filtresini oluşturulurken göz önünde bulundurulması gereken koşullar yer almaktadır.
| EventID | Occurrence | Comments |
| 538 | User Logoff | This event does not necessarily indicate the time that the user stopped using the computer. For example, if the user turns the computer off without first logging off, or if the network connection to a share breaks, the computer might not record a logoff at all, or might record a logoff only when the computer notices that the connection is broken. |
| 528 540 |
Where User Name contains $ or = X | Some Service and System accounts generate excessive activity while doing normal approved activities. Filtering these accounts can greatly reduce load when collecting successful logon events. Consider adding Event 538 and 680 if not already filtering those events. |
| 538 540 |
Where Logon Type = 3 and User Name contains $ | Windows Computers generate many logon/logoff events on DCs as they frequently check for group policy updates and query other information in AD. |
| 551 | User Initiates Logoff | Use Event 538, which confirms logoff instead. |
| 562 | A handle to an object closed | Always records a success. |
| 571 | Client Context deleted by Authorization Manager. | Normal where Authorization Manager is in use. |
| 573 | Process generates nonsystem audit event with Authorization Application Programming Interface (AuthZ API) | Typical behavior. |
| 577 578 |
Privilege service called, privileged object operation | These high volume events typically do not contain enough information either to understand what happened or to act upon them. |
| 594 | A handle to an object was duplicated | Typical behavior. |
| 595 | Indirect access to an object was obtained | Typical behavior. |
| 596 | Backup of data protection master key | Occurs automatically every 90 days with default settings. |
| 597 | Recovery of data protection master key | Typical behavior. |
| 624 642 |
Event 624 where User equals System, followed by 642 where Target Account Name equals IUSR_machinename or IWAM_machinename and Caller User Name equals machinename$ | This event sequence indicates that an administrator has installed IIS on the computer. |
| 624 630 642 |
User equals System and all three events have same time-stamp and New/Target Account Name equals HelpAssistant and Caller User Name equals DCname$ | This sequence is generated when an administrator installs Active Directory on a computer that runs Windows Server 2003. |
| 624 or 642 |
User equals ExchangeServername$ and Target Account Name is a Globally Unique Identifier (GUID) | This event occurs when an Exchange Server first comes online and automatically generates system mailboxes. |
| 624 | Caller User Name is any user and New Account Name is machinename$ |
A user in the domain has created or connected a new computer account in the domain. This event is acceptable if users have the right to join computers to a domain; otherwise you should investigate this event. |
| 627 | User equals System and Target Account Name equals TsInternetUser and Caller User Name is usually DCname$ |
These events result from the normal behavior of a computer that runs Terminal Services. |
| 672 | Kerberos AS Ticket request | If you collect logon events 528 and 540 from all computers, event 672 might not contain any additional useful information, as it just records that a Kerberos TGT was granted. There must still be a service ticket granted (event 673) for any access to occur. |
| 672 to 677 |
Where User Name contains $ | Windows Computers generate many Kerberos events as they frequently check for group policy updates and query other information in AD. |
| 680 | Account Logon | If you collecting logon events 528 and 540 from all computers, event 680 might not contain any additional useful information, because it just records validation of the account credentials. A separate logon event records what the user accessed. |
| 697 | Password policy checking API called |
Typical behavior. |
| 768 | Forest namespace collision | Not security related. |
| 769 770 771 |
Trusted forest information added, deleted or modified | These events indicate normal operation of inter-forest trusts. You should not confuse these with addition, deletion, or modification of the trust itself. |
| 832 to 841 |
Various Active Directory replication issues | No security implications. |
Tablo-1
Adtadmin ile filtre oluşturulurken kullanılabilecek alanlar aşağıda yer alan tablo-2’de yer almaktadır.
| Field Name | Type | Description | Sample |
| EventID | uint32 | 636 | |
| SequenceNo | uint32 | Dynamic Value, do not filter on this field | 7060303 |
| Flags | uint32 | See AuditRecordFlags enumeration below | 0x01 |
| Type | uint32 | 8=success, 16=failure, all ACS Events 4=info | 8 |
| Category | uint32 | Category ID | 7 |
| CreationTime | uint64 | FILETIME, UTC, time audit was created | 08.05.2008 21:14 |
| CollectionTime | uint64 | FILETIME, UTC7 time audit arrived at AdtServer | 08.05.2008 21:14 |
| AgentMachine | String | Name of machine that sent the event | MMS2008\SQL2005$ |
| EventMachine | String | Name of machine in event header | SQL2005 |
| Log | String | Log where Event originated | Security |
| Source | String | Log Source where Event originated | Security |
| HeaderSid | String | User SID in Header of Event | S-l-5-21-3936682612- |
| HeaderUser | String | User Name in Header of Event | Administrator |
| HeaderDomain | String | User Domain in Header of Event | MMS2008 |
| PrimarySid | String | Primary User SID in Event Details | S-l-5-21-1468679-39309 |
| PrimaryUser | String | Primary User Name in Header of Event | test41 |
| PrimaryDomain | String | Primary User Domain in Header of Event | SQL2005 |
| PrimaryLogonld | unint64 | Primary User LogonID in Event Details | 0 |
| ClientSid | String | Client User SID in Event Details | S-l-5-21-3936682612- |
| ClientUser | String | Client User Name in Header of Event | Administrator |
| ClientDomain | String | Client User Domain in Header of Event | MMS2008 |
| ClientLogonld | unint64 | Client User LogonID in Event Details | 541879972 |
| TargetSid | String | Target SID in details of Event | S-l-5-32-547 |
| TargetUser | String | Target Name in details of Event | Power User |
| TargetDomain | String | Target Domain in details of Event | Buiitin |
| StringOl through String22 | String | Event detail attributes |
Tablo-2
Filtre kullanımı için örnek bir komut aşağıda yer almaktadır.
“adtadmin /setquery /collector:”brckomacs01″ /query:”SELECT * FROM AdtsEvent WHERE NOT(EventId=514 Or EventId=515 OR EventId=516 OR EventId=518 OR EventId=519 OR EventId=538 OR EventId=551 OR EventId=566 OR EventId=538 OR EventId=598 OR EventId=600 OR EventId=602 OR EventId=4610 OR EventId=4611 OR EventId=4614 OR EventId=4615 OR EventId=4647 OR EventId=4800 OR EventId=4802 OR EventId=4803 OR EventId=5056 OR EventId=5061 OR (EventId>=592 AND EventId<=596) OR (EventId>=5058 AND EventId<=5059))”
SCOM 2007 R2 ile birlikte gelen ACS özelliğini tüm detaylarıyla üç makale halinde inceledik.Umarım sizler içinde yararlı olmuştur.
Bir başka makalede görüşmek üzere..
Ka®a
 ;?>
;?>
Pingback: SCOM 2012'ye SP1 Yükleme Bölüm - 2 | Mustafa Kara - System Center Cloud and Datacenter Management MVP